- leetcode
-
Introduction
- 0.1. LinkedList
-
1. Array
- 1.1. Largest Number
- 1.2. Two Sum
- 1.3. Three Sum
- 1.4. Three Sum Closest
- 1.5. Four Sum
- 1.6. Rotate Array
- 1.7. Container With Most Water
- 1.8. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
- 1.9. Remove Element
- 1.10. Next Permutation
- 1.11. Search in Rotated Sorted Array
- 1.12. Search for a Range
- 1.13. Search Insert Position
- 1.14. First Missing Positive
- 1.15. Trapping Rain Water
- 1.16. Jump Game
- 1.17. Jump Game II
- 1.18. Anagrams
- 1.19. Maximum Subarray
- 1.20. Merge Intervals
- 1.21. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
- 1.22. Insert Interval
- 1.23. Sort Colors
- 1.24. Set Matrix Zeroes
- 1.25. Search a 2D Matrix
- 1.26. Word Search
- 1.27. Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
- 1.28. Merge Sorted Array
- 1.29. Flood Fill a Matrix
- 1.30. Suffix Array
- 1.31. Union & Intersect Two Sorted Array
- 1.32. Get Exclusive Product Array
- 1.33. Triangle
- 1.34. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
- 1.35. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
- 1.36. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
- 1.37. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
- 1.38. Surrounded Regions
- 1.39. Longest Consecutive Sequence
-
2.
Tree
- 2.1. Binary Search Tree Iterator
- 2.2. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
- 2.3. Balanced Binary Tree
- 2.4. Symmetric Tree
- 2.5. Same Tree
- 2.6. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
- 2.7. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
- 2.8. Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
- 2.9. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
- 2.10. Scramble String
- 2.11. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
- 2.12. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
- 2.13. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
- 2.14. Unique Binary Search Trees
- 2.15. Validate Binary Search Tree
- 2.16. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
- 2.17. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
- 2.18. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
- 2.19. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
- 2.20. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
- 2.21. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
- 2.22. Path Sum
- 2.23. Path Sum II
- 2.24. Recover Binary Search Tree
- 2.25. Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly-Linked List
- 2.26. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
- 2.27. Print Binary Tree Root To Leaf Paths
- 2.28. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
- 2.29. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
-
3. Math
- 3.1. Factorial Trailing Zeroes
- 3.2. Pow
- 3.3. Reverse Integer
- 3.4. Excel Sheet Column Number
- 3.5. Excel Sheet Column Title
- 3.6. Base Converter
- 3.7. Palindrome Number
- 3.8. Divide Two Integers
- 3.9. Multiply Strings
- 3.10. Rotate Image
- 3.11. Sqrt(x)
- 3.12. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
- 3.13. Single Number
- 3.14. Single Number II
- 4. Dynamic Programming
- 5. Stack
-
6. String
- 6.1. Length of Last Word
- 6.2. Compare Version Numbers
- 6.3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
- 6.4. Longest Palindromic Substring
- 6.5. ZigZag Conversion
- 6.6. String to Integer (atoi)
- 6.7. Integer To Roman
- 6.8. Roman to Integer
- 6.9. Longest Common Prefix
- 6.10. Substring with Concatenation of All Words
- 6.11. Count And Say
- 6.12. Wildcard Matching
- 6.13. Permutation Sequence
- 6.14. Add Binary
- 6.15. Text Justification
- 6.16. Simplify Path
- 6.17. Minimum Window Substring
- 6.18. Implement strStr()
- 6.19. Valid Palindrome
- 6.20. Word Ladder
- 6.21. Word Ladder II
- 6.22. Palindrome Partitioning
- 6.23. Palindrome Partitioning II
- 6.24. Repeated DNA Sequences
-
7. LinkedList
- 7.1. Reverse Linked List
- 7.2. Reverse Linked List II
- 7.3. Add Two Numbers
- 7.4. Remove Nth Node From End of List
- 7.5. Merge Two Sorted Lists
- 7.6. Swap Nodes in Pairs
- 7.7. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
- 7.8. Rotate List
- 7.9. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
- 7.10. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
- 7.11. Partition List
- 7.12. Copy List with Random Pointer
- 7.13. Linked List Cycle
- 7.14. Linked List Cycle II
- 7.15. Reorder List
- 8. Bit
- 9. Recursion
- 10. Heap
- 11. Graph
Gray Code
The gray code is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit.
Given a non-negative integer n representing the total number of bits in the code, print the sequence of gray code. A gray code sequence must begin with 0.
For example, given n = 2, return [0,1,3,2]. Its gray code sequence is:
00 - 0 01 - 1 11 - 3 10 - 2Note:
For a given n, a gray code sequence is not uniquely defined.
For example, [0,2,3,1] is also a valid gray code sequence according to the above definition.
For now, the judge is able to judge based on one instance of gray code sequence. Sorry about that.
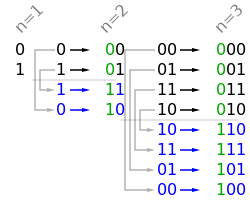
It is using the mirror arrangement way to calculate the gray code, because the grey code for (n-1) is already calculated, so we can calculate the next one by appending 1 to the last element in (n-1)'s grey code sequence, then the second last and so on.
for n=2: 1<<1 = 10
new gray code: 01+10=11, 00+10=10
for n=3: 1<<2 = 100
new gray code: 010+100=110, 011+100=111, 001+100=101, 000+100=100
public List<Integer> grayCode(int n) {
List<Integer> results = new ArrayList<Integer>();
results.add(0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int highBit = 1 << i;
for (int j = results.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
results.add(highBit + results.get(j));
}
}
return results;
}